As is the case with many emerging tech-nologies, the mine communications sector
has expanded so quickly and widely that
it’s difficult to establish boundaries
between traditional communications sys-tems and newer technologies that don’t
specifically involve person-to-person
speech, but nevertheless provide informa-tion, warnings and other signals that allow
miners to work in a safer environment. New
laws relating to underground mine safety
have driven increased activity in this field,
and the results are tools now available to
the modern miner that a previous genera-tion could not have imagined, such as
handheld VoIP phones and wireless hazard
monitors that can transmit for months from
remote parts of the mine without attention.
Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and
radar-detection technologies are further
examples of concepts that once might have
been considered science fiction but are
now commonly encountered in almost
every industrial setting.
Here are just a few wide-ranging exam-ples illustrating the expanding scope of
mine communications, ranging from the
ease with which comprehensive and reli-able satellite communications systems can
be configured to serve even temporary mine
operations, to the real-time reporting and
reliability offered by the latest in surface
and underground mine sensor systems.
Upgrading a Remote Mine’s Phone, Internet Service
OCENS, a Seattle, Washington, USA-based
provider of fixed and mobile satellite com-munications solutions, was selected by
Midas Gold of Spokane, Washington, to
configure a remote communications sys-tem consisting of a VSAT antenna and serv-ice, VoIP telephone system, and network
controls and metering at the Midas
Stibnite-Yellow Pine gold mine in the
Salmon River Mountains of central Idaho.
The mine site is at an altitude of
6,500 ft, surrounded by steep, forested
terrain. It operates seasonally from early
June until late October and has one per-manent structure, three modular offices,
and hosts a temporary camp that houses
25–30 workers.
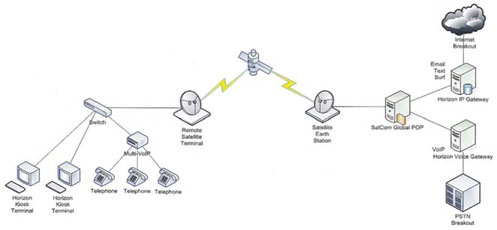

OCENS, a Northwest USA-based satellite communications solutions provider, designed a versatile satcomm system for Midas Gold, which operates a seasonal
gold-mining operation in a remote area. Designed around a 1.2-m-diameter antenna, the system provides high-speed Internet access, a protected network and a
cost-effective multi-line phone system.
The mine was using a Hughes Net VSAT
system as its sole Internet connection, and
mine operators used handheld satellite
phones for all voice communications.
According to OCENS, the existing VSAT
service has a restrictive use policy—and
handheld satellite phones aren’t the most
practical or cost-effective approach for reg-ular office use. Additionally, most of the
mine’s personnel had no access to Internet
or telephones while at the camp for their
two to three week work intervals. The mine
operators needed a more robust communi-cations system providing high speed
Internet with minimal usage restrictions,
Internet-access PIN controls and metering
for individual users, a multi-line phone sys-tem and network access for the work camp.
OCENS installed a new VSAT system
with a 1.2-m antenna and high-speed 2-Mbps service that includes a usage limit of
30 gigabytes per month. The site’s local
network was designed around OCENS’
WebXaccelerator (WXa)—an Internet accel-eration, metering and automatic failover
device. All traffic is routed through the
WXa, which provides metered Internet
access via pre-assigned PINs, along with
usage logs, remote support, and load bal-ancing that takes advantage of the existing
Hughes system that also serves as an auto-matic backup. Additional features built
into the WXa include Web compression,
black lists/white lists and Wi-Fi.
Wireless Access Points were placed at
each of the three offices as well as the
camp. Since the camp is located approxi-mately 1,000 ft away and down a slope
from the main office area where the VSAT
equipment is located, a high-range wire-less bridge was installed to integrate the
camp into the network.
OCENS said it also installed its Horizon
Multi VoIP platform, which uses the VSAT
connection and provides low-cost voice
service. Four of eight available lines are
used at the site with one line going to each
office. The lines use standard CAT3
cabling and are compatible with any ordi-nary phone handset.
Built to withstand adverse climatic
conditions, vibration and high tempera-tures—and originally designed for ship-board use—the Multi VoIP unit is installed
by simply connecting it to an Ethernet
Local Area Network (LAN) that provides
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) IP addressing. The Multi VoIP
optimized plug and play configuration,
according to OCENS, allows access to
more simultaneous voice connections over
standard IP networks than any other sys-tem currently available.
The Horizon unit uses an industry-lead-ing codec that enables the system to pro-vide high efficiency over satellite and ter-restrial networks. The main features of the
system include:
•Eight available standard analog phone
ports for concurrent voice connections.
•Three quality settings for optimum
cost/quality voice delivery.
•Optimized two-way voicemail for all
Horizon users.
•Extension number for direct dialing of
incoming calls.
•‘Follow me’ user extension.
•Optimized local number dialing to
access users.
•Pre-paid and post-paid PIN protection.
•Low cost international calling.
 An IBIS-M slope monitoring radar deployed at Minera Yanacocha, Peru.
An IBIS-M slope monitoring radar deployed at Minera Yanacocha, Peru.
(Courtesy of Minera Yanacocha)
According to OCENS, a major benefit of
using Horizon over satellite is its
SmartPacket technology which compresses
VoIP calls while maintaining voice quality.
For example, even at its highest call quali-ty setting, a single line on the Horizon uses
only about 25% of the bandwidth of a typ-ical VoIP phone. Prepaid and postpaid
service is universally available to call any-where in the world and any call is free
when calling “in-network” from one
Horizon unit to another.
OCENS preconfigured and tested Midas
Gold’s entire network before deploying it to
the site to ensure a smooth “plug-and-play” installation. With remote access
enabled and network monitoring capabili-ties from the OCENS office, remote-sup-port is offered with real-time visibility
ensuring reduced downtime in the event of
a problem. The final implementation of the
complete system, according to OCENS,
provided high-speed Internet access, a pro-tected network and a cost-effective multi-line phone system—capabilities compara-ble to a conventional land-based service,
but now accessible in the remote region
where the mine is located. Similar sys-tems, according to the company, are appro-priate and available for virtually any geo-graphical location on earth.
Using Radar to Monitor Slope Stability
Since the first applications in early 2000,
slope monitoring radar have been used
extensively for monitoring instability issues
in either natural and engineered slopes and
to support the management of the associ-ated geotechnical risk. IDS Ingegneria dei
Sistemi SpA, an Italian company with more
than 30 years of experience in radar tech-nologies, recently introduced IBIS-M for
the mining market. More than 45 units
have been commissioned around the world
and it’s gaining acceptance with more
prominent mining groups, which have
adopted the IDS technology to increase
safety standards. This trend reflects the
crucial role played by slope monitoring
radar in modern surface mining.
The IBIS-M features very high spatial
resolution and accuracy and the greatest
operating distance currently available on
the market along with the fastest scan
time, making it possible to effectively track
slope movements and manage geo-technical risks. The working distances
range from few hundred meters to more
than 3.5 km from the slope. Moreover, the
few moving parts of the radar and its very
low power consumption make it able to dra-matically reduce the use of a diesel gener-ator relying mainly on solar power, resulting
in high reliability and high mechanical
robustness. Finally, the use of small anten-nas instead of wide parabolic dishes elimi-nates the risk of wind-induced vibrations,
particularly troublesome in windy regions
where it may result, depending on the wind
speed, in noisy displacement measure-ments or in the need to turn off the radar to
avoid damages to the system.
IBIS-M has the ability to measure the
entire range of spatial scales of typical
slope instabilities within a pit, from bench
scale to overall slope failures passing
through multi-bench and inter-ramp scale
failures and the entire temporal scale of
the slope instabilities, from fast move-ments (mm/day - cm/day), to very slow
movements (mm/month - mm/year). Based
on this accurate data IBIS-M is able to
generate alarms for progressive movements
potentially leading to slope failures,
improving the safety conditions of modern
mines, and allowing the local staff to opti-mize production.
The radar has detected movements and
generated alarms in tens of cases on slope
movements ranging from bench scale fail-ures involving just a few tons of material to
multi-bench failures with many millions of
tons collapsed. Today IBIS-M is considered
by IDS customers an effective tool to
improve the safety of their operations.
 Tunnel Radio’s methane and CO sensors relay information from the
Tunnel Radio’s methane and CO sensors relay information from the
face to the surface wirelessly.
MST Expands Globally and Gains New Approvals
Australian-based Mine Site Technologies
(MST) is a solutions provider, specializing
in the development and supply of technol-ogy, and services, to the mining industry. In
addition to gaining ATEX approval for its
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones, the company recently opened a new office
in Ontario and acquired Nixon Communi-cations, a network and communications
infrastructure provider for the mining, oil
and gas, remote construction and Coal
Seam Gas sectors.
Building on MST’s underground mining
strengths, the Nixons acquisition is a core
element of MST’s ongoing development of
its surface mining and resources business,
substantially expanding its capabilities.
Nixons provided communication systems
and equipment to mining projects operat-ing primarily across Queensland, as well as
in other Australian locations, New Guinea
and the Solomon Islands. Founded by John
Nixon in 1977 as a one-man operation, the
Gladstone-headquartered company has
grown steadily to now employ 70 people,
with branch offices in Rockhampton,
Mackay and Blackwater. Nixon, will remain
with the combined company for at least 18
months as an adviser and consultant.
The company’s MinePhone VoIP digital
phone and NS40 Wireless Access Point for
integrated underground mining communica-tions recently achieved ATEX certification,
Group 1 Category M1 as intrinsically safe,
which certifies that it can be safely used in
underground coal mines. “These approvals
open a new door of opportunity for MST in
Europe, with the installation of these tech-nologies now being progressed in mines in
Germany, Poland and Russia,” said MST’s
CEO, Lloyd Zenari. “We make modern and
fit-for-purpose technologies available to our
customers with a focus on enhancing safety
and productivity through applied technology.
We provide the opportunity for increasing
productivity—safely.” Formal testing of the
MinePhone and NS40 was carried out by
DEKRA-EXAM of Germany.
MSHA Approves Wireless Methane Detector
Last year, the U.S. Mine Safety and Health
Administration (MSHA) approved Tunnel
Radio’s TR-MX-332 methane and CO (car-bon monoxide) detection wireless reader as
intrinsically safe for coal mine use.
Designed for use with the MineAx Bird Dog
RFID personnel tracking system, this new
micro-technology now makes it feasible to
wirelessly deploy a multitude of methane
and CO sensors anywhere needed in a coal
mine environment. For the first time, this
critical gas level information can be trans-mitted wirelessly to the surface from the
longwall face and the continuous miner
headings. Complementing the company’s
long -range wireless readers, these sensors
may operate for months on battery power to
provide electronic tracking of personnel
location and gas levels simultaneously to
control centers on the surface.
As coal mines under the MINER Act of
2006 are required to deploy electronic
tracking technologies in the United States,
the widely used Tunnel Radio MineAx
tracking system can additionally provide
very precise methane and hydrocarbon
group gas measurement 24/7 in the mines
using this new digital technology. Wireless
sensors can be located exactly where need-ed, a shortcoming of current wired tech-nologies that also must be disabled once
an emergency occurs. In addition, the
same device is equipped with a CO sensor
(a precursor gas emitted from very low level
combustion sources), to alert mine crews
immediately of unsafe thermal conditions,
giving time to react before a fire breaks
out. The unit also transmits temperature,
humidity and barometric pressure read-ings, providing atmospheric data helpful in
evaluating overall mine ventilation system
effectiveness, a critical factor in recent
mine disasters.
 MST’s VoIP MinePhone.
MST’s VoIP MinePhone.
With this equipment deployed, mine
personnel now have the tools to prevent
deadly methane ignitions. Critical infor-mation can now be analyzed from the
comfort of the office, home or head-quarters by simply accessing the mine
central computer through the Internet,
including the use of most mobile devices.
The MineAx Bird Dog tracking system is
already deployed in more than 50 mines
in three countries. “We feel this tech-nology is a win for miner safety, the
industry and is a credit to American know
how,” said Mark Rose, president, Tunnel
Radio. Tunnel Radio of America is based
near Corvallis, Oregon, and has provided
technologies and services to the mining
and railroad industries for more than
20 years.




